Combination Reaction
A combination reaction is where two reactants react together to form one product which is an ionic compound.The combination between Magnesium (Mg2+) and Oxygen (O2-) will produce Magnesium Oxide
Mg2+ + O2- -------------> MgO
 |
| https://edu.glogster.com/glog/chemical-reaction/1prkmxx63bh?=glogpedia-source |
Decomposition Reaction
A decomposition experiment is where a single chemical compound breaks down into two or more single produces or simpler compounds.
 |
| https://www.mindmeister.com/457897743/chemical-reaction-types |
Metal Carbonate + Heat = Metal Oxide + CO2
Copper Cabonate + Hear = Copper Oxide + CO2
CUCO3 -------> CUO + CO2
Substance: Copper Carbonate = CuCO3
This is called thermal decomposition.
Thermal decomposition is an example of an endothermic reaction, a reaction that gains energy from surroundings.
Displacement Reactions
In a displacement reaction...
a more reactive metal displaces (take over/force out) a less reactive metal.
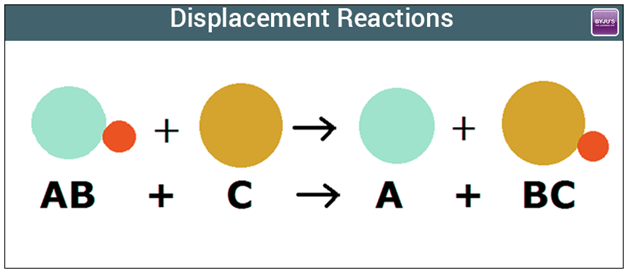 |
| https://byjus.com/chemistry/displacement-reactions/ |
Exchange Reaction
Exchange reactions are where the cations and anions that were partners in the reactants they are exchange in the product.
AB+CD > AD + BC
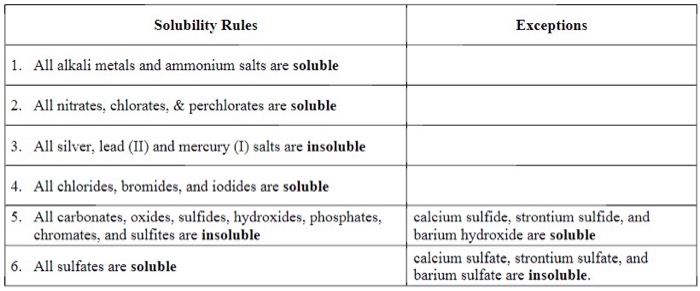
Stability Rules
The following are the solubility rules for common ionic solids. If there two rules appear to contradict each other, the preceding rule takes precedence.
- Salts containing Group I elements (Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Rb+) are soluble . There are few exceptions to this rule. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are also soluble.
- Salts containing nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble.
- Salts containing Cl -, Br -, or I - are generally soluble. Important exceptions to this rule are halide salts of Ag+, Pb2+, and (Hg2)2+. Thus, AgCl, PbBr2, and Hg2Cl2 are insoluble.
- Most silver salts are insoluble. AgNO3 and Ag(C2H3O2) are common soluble salts of silver; virtually all others are insoluble.
- Most sulfate salts are soluble. Important exceptions to this rule include CaSO4, BaSO4, PbSO4, Ag2SO4 and SrSO4 .
- Most hydroxide salts are only slightly soluble. Hydroxide salts of Group I elements are soluble. Hydroxide salts of Group II elements (Ca, Sr, and Ba) are slightly soluble. Hydroxide salts of transition metals and Al3+ are insoluble. Thus, Fe(OH)3, Al(OH)3, Co(OH)2 are not soluble.
- Most sulfides of transition metals are highly insoluble, including CdS, FeS, ZnS, and Ag2S. Arsenic, antimony, bismuth, and lead sulfides are also insoluble.
- Carbonates are frequently insoluble. Group II carbonates (CaCO3, SrCO3, and BaCO3) are insoluble, as are FeCO3 and PbCO3.
- Chromates are frequently insoluble. Examples include PbCrO4 and BaCrO4.
- Phosphates such as Ca3(PO4)2 and Ag3PO4 are frequently insoluble.
- Fluorides such as BaF2, MgF2, and PbF2 are frequently insoluble.
Soluble = Dissolves
Insoluble = Doesn't Dissolve (solid in a solution)
Example :
Sodium Hydroxide was reacted with silver nitrate. An exchange of ions occurred. Sodium nitrate was formed. Rule 1 says that all nitrates are soluble. This means that it won't form a solid.
Silver Hydroxide was also formed during this exchange reaction. Rule 6 says that all hydroxides are insoluble except sodium and potassium hydroxides. Because silver hydroxide is neither a sodium or potassium hydroxide this means that silver hydroxide is insoluble. That means a solid of AgOH was formed.